Golkonda
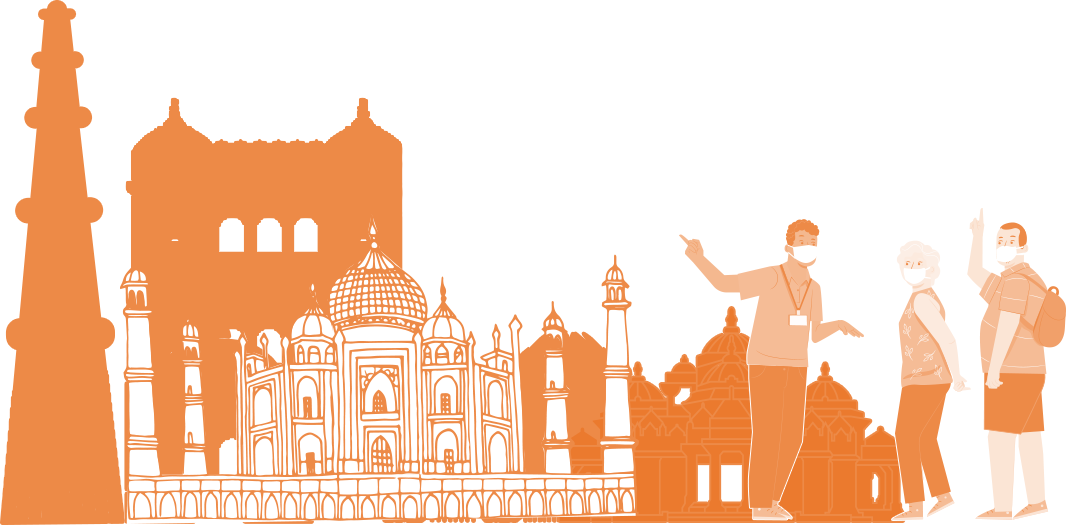
Golconda, also known as Golkonda or Golla konda, a fort of Southern India and capital of medieval Golconda Sultanate (c.1518–1687), is situated 11 km west of Hyderabad, Telangana. It is also a mandal of Hyderabad District. The region is known for the mines that have produced some of the world’s most famous gems, including the Koh-i-Noor, Hope Diamond and the Nassak Diamond.
The Golconda fort was first built by Kakatiya as part of their western defenses. It was built in 945 CE-970 CE on the lines of the Kondapalli fort. The city and fortress are built on a granite hill that is 120 meters (400 ft) high and is surrounded by massive crenelated ramparts. The fort was rebuilt and strengthened by Pratapa Rudra of Kakatiya dynasty. The fort was further strengthened by Musunuri Nayaks who overthrew the Tughlak army occupying Warangal. The fort was ceded by the Musunuri chief, Kapaya Nayaka to the Bahmanis as part of the treaty in 1364 AD. The fort became the capital of a major province in the Sultanate and after its collapse the capital of the Qutb Shahi kings. The fort finally fell into ruins after a siege and its fall to Mughal emperor Aurangazeb in 1687 AD.
After the collapse of the Bahmani Sultanat, Golkonda rose to prominence as the seat of the Qutb Shahi dynasty around 1507. Over a period of 62 years the mud fort was expanded by the first three Qutb Shahi kings into a massive fort of granite, extending around 5 km in circumference. It remained the capital of the Qutb Shahi dynasty until 1590 when the capital was shifted to Hyderabad. The Qutb Shahis expanded the fort, whose 7 km outer wall enclosed the city. The state became a focal point for Shia Islam in India, for instance, in the 17th century, Bahraini clerics, Sheikh Ja`far bin Kamal al-Din and Sheikh Salih Al-Karzakani both emigrated to Golkonda.